
Liquid nitrogen for NMR spectroscopy
Liquid nitrogen plays a critical role in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy by cooling the superconducting magnets that generate the strong magnetic fields required for analysis. Maintaining these magnets at ultra-low temperatures ensures stable, high-resolution measurements, allowing researchers to accurately determine the structure, composition, and properties of molecules.

Liquid nitrogen applications in NMR
Liquid nitrogen is used for:
-
Maintaining Superconductivity: LN₂ provides the ultra-low temperatures needed to keep NMR magnets superconducting, enabling the generation of strong, stable magnetic fields.
-
Ensuring Accurate Measurements: By keeping magnets at consistent low temperatures, LN₂ helps produce high-resolution, reliable data for molecular structure and property analysis.
-
Preventing Equipment Damage: A continuous LN₂ supply protects sensitive superconducting magnets from overheating or quenching, avoiding costly repairs and downtime.
How does NMR technology work?
NMR spectroscopy is based on the principle that certain atomic nuclei
(like ¹H, ¹³C, ¹⁵N) absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation when
placed in a strong magnetic field and exposed to radiofrequency (RF)
pulses. By measuring these signals, scientists can infer detailed
information about molecular structures and dynamics.
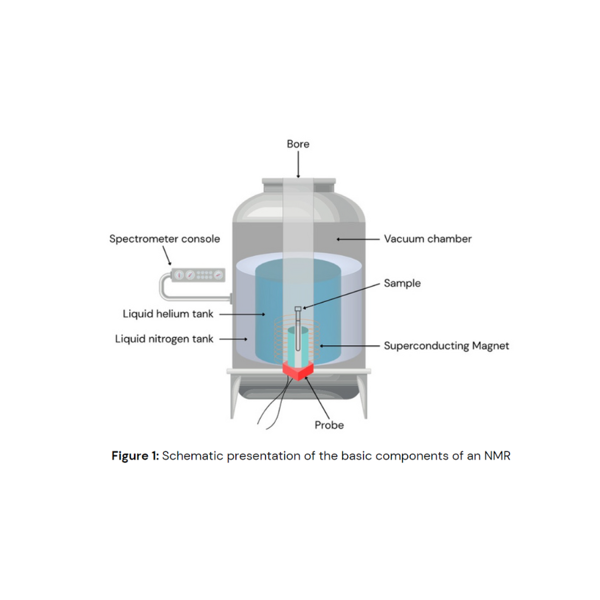
Key hardware components of an NMR Spectrometer include:
- The superconducting magnet, which generates a strong, stable magnetic field, and operates at extremely low temperatures (around -269°C).
- The cryostat: a vacuum-insulated vessel that houses the superconducting magnet, containing an inner chamber filled with liquid helium, and a heat shield cooled by LN₂ to insulate the liquid helium and reduce its boil-off rate. The LN₂ layer keeps the helium usage economical and prevents premature helium loss.
- The sample spinner and temperature control unit: spin the sample to ensure homogeneity and control its temperature during measurement.
- The probe contains RF coils and is inserted into the bore of the magnet. It generates RF pulses that excite the nuclear spins in the sample, and detects the emitted signals from the excited nuclei and transmits them to the spectrometer for analysis.
- The spectrometer console is the central processing unit of the system, controlling and analysing the signals generated during an experiment.
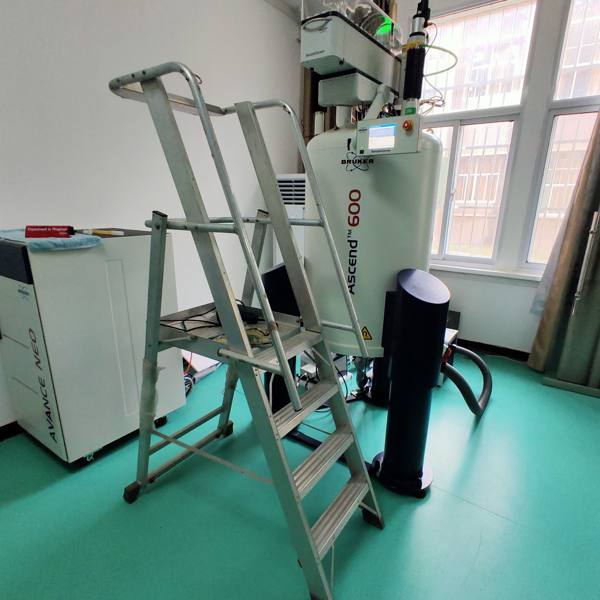

What is magnet quenching in NMR instruments?
A quench occurs when part or all of the superconducting coil of the superconducting magnets transitions into a normal (resistive) state, a process that can happen due to:
- Temperature rise (e.g. insufficient cooling),
- Mechanical disturbances,
- Power failure,
- Sudden helium loss.
When this transition happens, the magnet rapidly heats up, and the energy stored in the magnetic field is released, often boiling off hundreds to thousands of litres of liquid helium within minutes. This is highly dangerous and damaging.

Why choose liquid litrogen generators?
While traditional methods of supplying liquid nitrogen, such as dewars, have been used, liquid nitrogen generators offer several advantages:
- Continuous Supply: Generators ensure a constant supply of liquid nitrogen, eliminating the need for frequent refills and minimizing downtime.
- Reduced Maintenance: Compared to dewars, generators require minimal maintenance, saving time and resources.
- Improved Safety: On-site generation eliminates the risks of handling and transporting large quantities of liquid nitrogen.
- Environmental Benefits: Generators reduce the carbon footprint by eliminating the need for frequent deliveries and transportation.
- Cost-Effective: Long-term savings can be achieved through reduced operational costs and increased efficiency.
By choosing a liquid nitrogen generator, laboratories can optimize their NMR operations, improve efficiency, and reduce overall costs.
Related products
Liquid nitrogen solutions for NMR




